Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds that give cannabis its distinctive effect. In a sense, they are a great deal of the magic behind the drug.
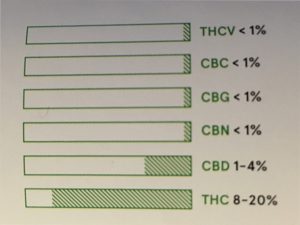
Some of the more well known cannabinoids include THC, which is in high concentration in sativa plants, and CBD, commonly found in indica strains. Since 1964, however, humans have discovered over 75 unique cannabinoids; some psychoactive, others not.
Since each cannabinoid contributes somehow to the overall pharmacology, we now know that cannabis is actually highly complex in its composition. Breeders have found that specific combinations of cannabinoids can bring about specific subjective effects.
Major Cannabinoids
When it comes to these ones, most of you already know what’s good.
Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (or THC) is primarily responsible for the ‘high’. It enhances creativity, sharpens the mind and increases the sensitivity of the senses – sound, colour and light take on a whole new meaning under the influence of THC. It can also increase sexual arousal in the right people.
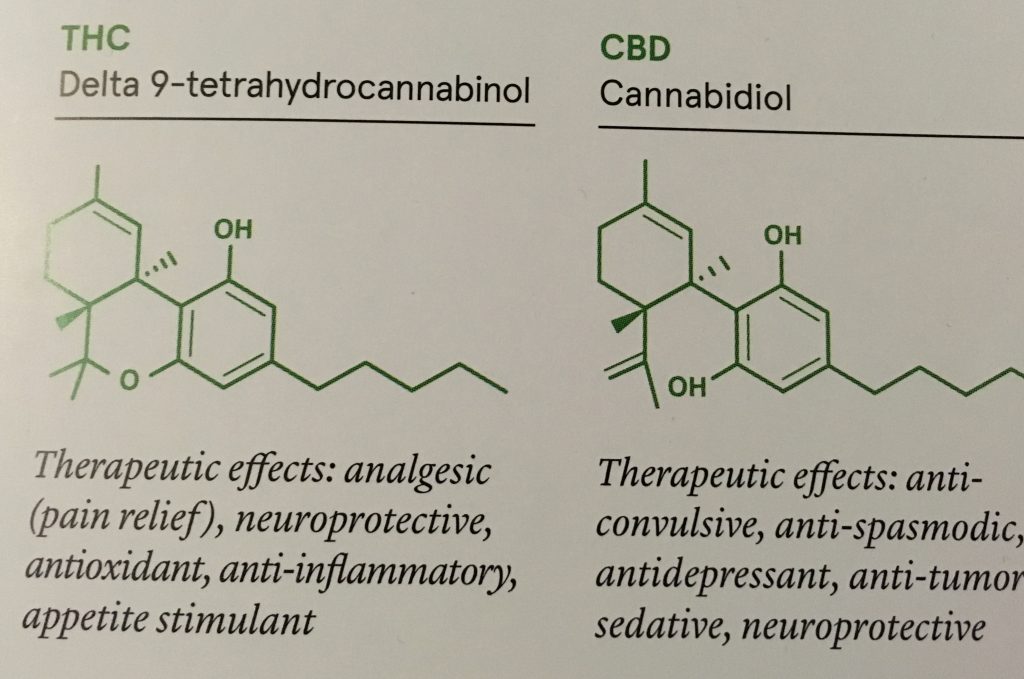
Cannabidiol (or CBD), on the other hand, is not psychoactive. It works as an antagonist to THC, actually reducing its psychoactive effect – for better or worse. Many would say for the better; not only does CBD increase the duration of the cannabis high, it is also known to protect from the worst harms of THC.
CBD is where the medicinal properties of cannabis have been apparent for some time. It is effective against anxiety and stress, helps relax the muscles, and is a functional treatment against seizures.
Minor Cannabinoids
These cannabinoids may not be as well known, but their ‘entourage’ effect makes their presence felt in your high. Here are just a few of the dozens you’re smoking on:
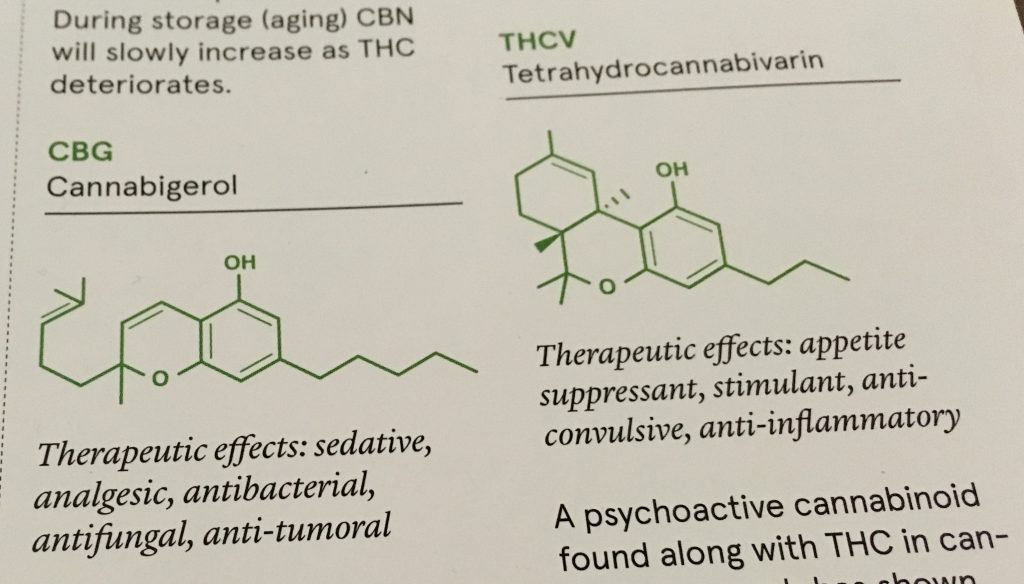
CBG (or Cannabigerol) is a precursor to other
well known cannabinoids, such as THC. It is generally abundant in low-THC hemp materials. It has only been found in trace amounts in most strains.
THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin) is a psychoactive cannabinoid, often found along with THC in cannabis. In low doses, THCV strongly potentiates THC, producing a heavier high over a shorter duration. In high doses, however, THCV is thought to oppose the effects of THC.
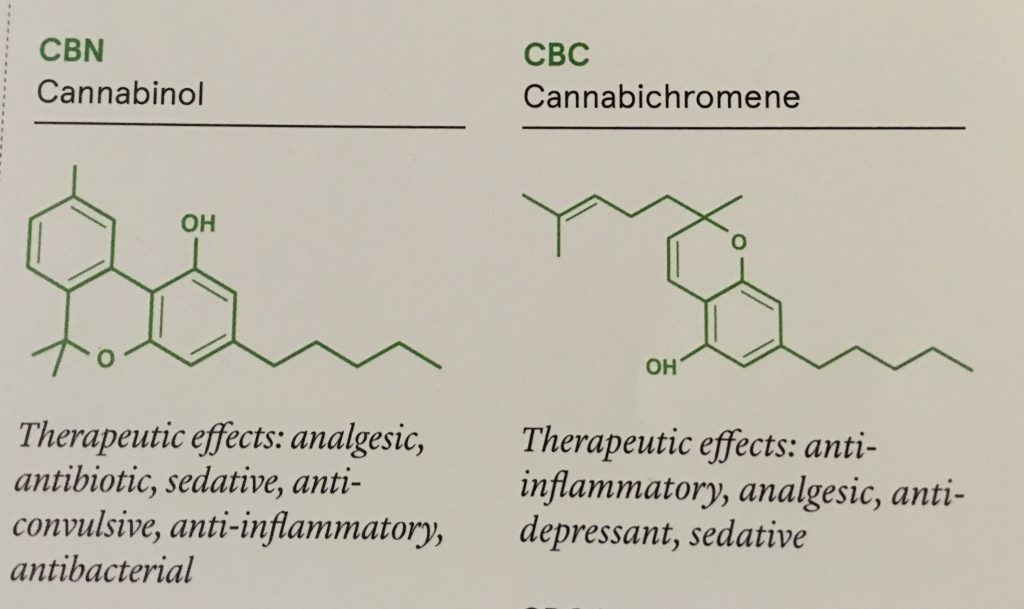
CBN (or Cannabinol) is mildly psychoactive and analgesic, working quite similarly to aspirin. It is known to relieve headaches and other bodily tensions. During storage, THC will deteriorate as CBN increases.
Finally, CBC (Cannabichromene) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that potentiates THC. Whilst the way it interacts with THC is unknown, it does seem to make the high more intense and pronounced. CBC is also considered a strong sedative and pain reliever.
Are you knowledgeable when it comes to the cannabinoids you’re ingesting? Share any fun facts you may have with others down in the comments!